

Specialization
- Diabetes & Dyslipidemia
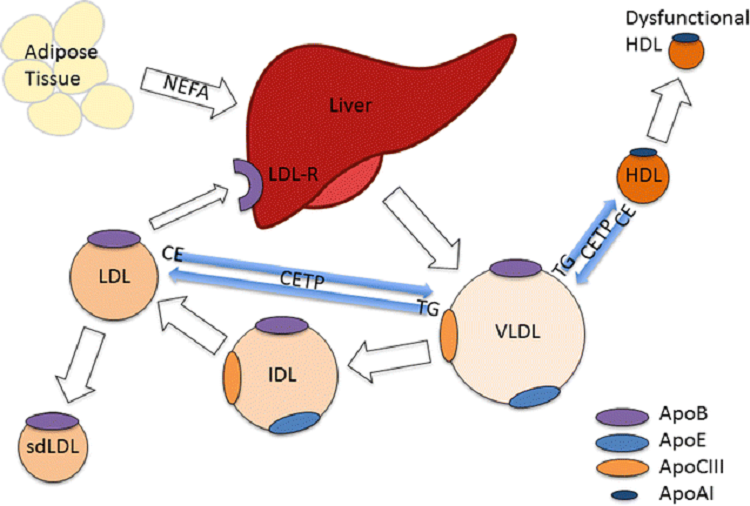
Diabetes is considered a “significant secondary cause” of dyslipidemia. especially those with type 2 diabetes have a combination of high TG, high small dense LDL fractions, and low HDL cholesterol.
- Diabetes & Pregnancy

The diabetes effect on baby during pregnancy in the early weeks can be quite harmful. It can affect the baby’s organ development inside the uterus and result in an enlarged heart.
- Diabetes & Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea can prevent a person from getting a good night sleep, which can worsen diabetes or perhaps increase the risk of developing diabetes.
- Diabetes & Obesity

The relationship between obesity and diabetes is of such interdependence that the term 'diabesity' has been coined. The passage from obesity to diabetes is made by a progressive defect in insulin secretion coupled with a progressive rise in insulin resistance.
- Diabetes & Neuropathy

Diabetic neuropathy is nerve damage that is caused by diabetes.Nerves are bundles of special tissues that carry signals between your brain and other parts of your body.
- Diabetes & Cancer
Diabetes can also put you at a risk of a wide range of health conditions like glaucoma, kidney disease and stroke. According to a study by the American Institute for Cancer Research, diabetics have a higher than average risk to develop kidney, pancreatic and colorectal cancer.
- Diabetes & Nephropathy

Diabetic nephropathy is a serious kidney-related complication of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. It is also called diabetic kidney disease. About 25% of people with diabetes eventually develop kidney disease.
- Diabetes & Retinopathy
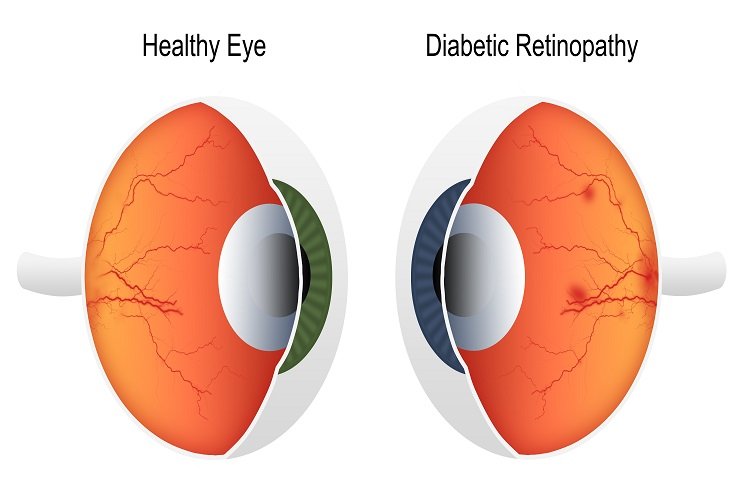
Retinopathy is generally detected by an eye specialist called an ophthalmologist. An eye examination for many people with retinopathy includes testing visual acuity or sharpness of vision, checking the sharpness of peripheral vision, and testing the pressure inside the eye.
- Type 2 Diabetes in Paediatrics

Type 2 diabetes is a disease that has as its main symptom a high level of sugar (glucose) in the blood. It is the most common form of diabetes. It is often called non-insulin-dependent diabetes, or adult-onset diabetes.
- Diabetes & Cardiovascular Disease

The connection between diabetes and heart disease starts with high blood sugar levels. Fatty material that builds up on the inside of these blood vessels can eventually block blood flow to the heart or brain, leading to heart attack or stroke.
- Prevention of other Diabetic Complications

Check Your Blood Sugar. Pricking your finger each day can help you and your doctor see if your blood sugar is under control. Eat Right. Eating well can help you keep a healthy weight and lower your cholesterol or blood pressure.
- Diabetes & Sexual Dysfunction

Sexual problems (sexual dysfunction) are common among people with diabetes, particularly in older men who have had diabetes for years. In addition, many medical experts believe that women with diabetes experience sexual difficulties as a result of complications from the disease.
- Diabetes Prevention

There is an urgent need for strategies to prevent or at least slow down the emerging burden of diabetes apart from treating diabetes and associated complications. Prevention of diabetes and its complications is the urgent need of the hour. Prevention of diabetes can be done at every stage in the natural history of diabetes resulting in four levels of diabetes prevention.
- Diabetes Diet

Nutrition and physical activity are important parts of a healthy lifestyle when you have diabetes. Along with other benefits, following a healthy meal plan and being active can help you keep your blood glucose level, also called blood sugar, in your target range. To manage your blood glucose, you need to balance what you eat and drink with physical activity and diabetes medicine, if you take any..
- Weight Loss

Weight loss is a decrease in body weight resulting from either voluntary (diet, exercise) or involuntary (illness) circumstances. Most instances of weight loss arise due to the loss of body fat, but in cases of extreme or severe weight loss, protein and other substances in the body can also be depleted.
- Stress Management

Stress is what you feel when you have to handle more than you are used to. When you are stressed, your body responds as though you are in danger. It makes hormones that speed up your heart, make you breathe faster, and give you a burst of energy. This is called the fight-or-flight stress response..
- Precision Diabetes
At its core, precision is a model that proposes customization of health care with medical practices, testing, decisions and treatments tailored to the individual patient level. Diagnostic tests and therapies are selected not only on the basis of generic symptoms but also by the specific risk factor profile and health history obtained from genetic profiling.
- Insulin Management

Short-acting insulin is administered before meals to cover the carbohydrate load. Short-acting analogue insulin is given up to 15 minutes before a meal to maintain two-hour postprandial glucose levels. Taking insulin after meals increases the risk of early postprandial hyperglycemia followed by delayed hypoglycemia
- Diabetes Hypoglycemia

Hypoglycemia is a clinical state with low glucose concentration in the blood, usually associated with giddiness, weakness, anxiety, irritability, hunger, palpitation, blurred vision, headache, inability to concentrate, loss of memory, and in severe cases, paralysis, seizures or coma. Patients with diabetes start getting symptoms of hypoglycemia when the sugar levels drop below 70 mg/dl but this can vary widely from person to person. Hypoglycemia usually occurs when a meal is missed or delayed, following unaccustomed heavy exercise or when too high a dose of insulin or diabetes tablets is taken in error.
- Diabetes Eye care
Diabetes can affect the eye in various ways. Diabetic Retinopathy is a common vision-threatening complication which causes damage to the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. The risk of developing retinopathy is higher for patients who have had uncontrolled diabetes for a long time. It has been estimated that about 70% of patients who have had diabetes for over 15 years will have some damage to their eyes due to diabetes. Efficient methods are available to detect high-risk retinal lesions and blindness due to diabetes which can be prevented if early detection is done and timely treatment is administered.
- Diabetes Footcare

Foot care is particularly important if you have diabetes. Foot problems are a common complication of this condition. Your feet can be affected in two ways. Blood supply may be affected, resulting in slower healing. You may also lose some feeling in your feet due to nerve damage. A person whose nerves are damaged by diabetes may not realise they have minor cuts or blisters, which can lead to ulcers.
- Diabetes Cardiacare

High blood glucose from diabetes can damage your blood vessels and the nerves that control your heart and blood vessels. Over time, this damage can lead to heart disease.People with diabetes tend to develop heart disease at a younger age than people without diabetes. Adults with diabetes are nearly twice as likely to have heart disease or stroke as adults without diabetes.
- Diabetes Kidney care

When your kidneys are damaged, they can’t filter blood like they should, which can cause wastes to build up in your body. Kidney damage can also cause other health problems. Kidney damage caused by diabetes usually occurs slowly, over many years. You can take steps to protect your kidneys and to prevent or delay kidney damage.
- Diabetes Physiotheraphy

Physiotherapy is a useful tool in the battle against diabetes for a number of reasons. Firstly, it allows the patient to achieve a healthy weight. Being obese or overweight is a major risk factor for diabetes, so many people who suffer from diabetes will also be at risk of other complications associated with being overweight. Exercising with a physiotherapist can help reduce the risk of further complications in other areas, as well as improve the overall quality of life for the patient. Furthermore, a common symptom amongst diabetics is fatigue, so many people may gradually become more sedentary and put themselves at risk of gaining weight.
- Diabetes Fitness

Exercise improves blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes, reduces cardiovascular risk factors, contributes to weight loss, and improves well-being . Regular exercise may prevent or delay type 2 diabetes development
- Diabetes Obesity Center

Obesity is the most frequently encountered metabolic disorder. Its incidence and prevalence are extremely high. Obesity is an important risk factor not only for diabetes but also for hypertension, coronary heart disease, dyslipidemia and other serious health complications. In India approximately 139 million people are obese. Obesity impairs quality of life and reduces life expectancy. Weight loss is extremely important to improve sugar control and to decrease other risk associations.
- Diabetes Laboratory

Diabetes is a condition that affects the body’s ability to either produce or use insulin. Insulin helps the body utilize blood sugar for energy. Diabetes results in blood sugar (blood glucose) that rises to abnormally high levels.
- Cardiac Care
A patient with diabetes has a four times higher risk of developing a heart problem compared to someone of the same age and sex without diabetes.
- Kidney Care
Diabetes Medical Centre has facilities to estimate the early and late markers of kidney disease and detect diabetic nephropathy.
- Diabetes Diet
The 3 D’s of the nutrition department -Dietary service, Diet counselling and Diet analysis- contribute significantly to the control of diabetes by prescribing a suitable diet, thus preventing complications.
- Diabetes Foot Care
The foot is one of the major organs that can get affected by diabetes. The Foot Clinic at Diabetes Medical Centre is fully equipped with facilities for early detection and diagnosis of diabetes foot complications
- Pregnancy Diabetes
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) only happens during pregnancy. It means you have high blood sugar levels, but those levels were normal before you were pregnant
- Precision Diabetes
At its core, precision is a model that proposes customization of health care with medical practices, testing, decisions and treatments tailored to the individual patient level.
- Physiotherapy
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterised by high blood sugar (glucose) levels. The condition results from the body’s inadequate production of insulin or the body’s altered response to insulin, or both.
- Orthopedic Care
We have experienced orthopaedic surgeons at hand to deal with bone and joint problems of patients with diabetes. Right from the mobilization of the joints to surgeries, all services are provided for diabetes patients.
- Fitness
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterised by high blood glucose (sugar) levels. Diabetes cannot be cured, but it can often be managed with proper medical care, diet, and regular exercise.
- Dental Care
Dental gum problem (periodontal disease) is considered to be one of the major complications of uncontrolled diabetes which can be followed by loss of teeth.
- Stress Management
The Department of Stress Management has been instituted to investigate the psychosocial aspects of diabetes, which may influence the prescribed regimen of self-care, and to conduct interventions for better self-management of diabetes, its complications and related disorders.
- Diabetes Laboratory
The Laboratory services at Diabetes Medical Centre is unique in using advanced technology and having fully automated walk away systems in the department of Biochemistry, Hematology, Pathology, Microbiology and Serology which provide round the clock services, seven days a week.
- Insulin Management
Based on the type of diabetes and the level of sugar control, certain patients may be suggested to start insulin treatment.
- Diabetes Obesity
Obesity is the most frequently encountered metabolic disorder. Its incidence and prevalence are extremely high.
- Eye Care
Diabetes can affect the eye in various ways. Diabetic Retinopathy is a common vision-threatening complication which causes damage to the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye.
- Weight Loss
Obesity is a chronic disorder with multiple serious health complications. Previously it used to be a concern only for developed countries, but now it is becoming a problem for developing countries as well.

Convenient & Affordable
Choose a date and time.
From immunizations to checkups and preventive care, exams, our primary care physicians and providers work to keep you and your whole family healthy and strong each and every day.



